How to enable LLMs to dynamically choose their reasoning strategy
METASCALE is a prompt-engineering framework that enhances the reasoning abilities of any LLM.
METASCALE, a new framework introduced in a paper by the University of California, Davis, the University of Southern California, and Microsoft Research, enables LLMs to choose different reasoning strategies based on the problem they are solving.
This is a great challenge in LLMs. They have fixed reasoning behavior, as opposed to humans who use different methods to solve different problems.
Current popular reasoning techniques, such as chain-of-thought (CoT) prompting and self-verification, are designed for specific tasks. They do not generalize to different types of problems.
The researchers propose the concept of "meta-thinking" to address this problem. Meta-thinking allows LLMs to “think” about the reasoning strategy before engaging in reasoning.
Instead of directly solving the problem, the LLM first determines the most appropriate cognitive strategy (e.g., you must be a mathematician to solve this problem). It then chooses a solution strategy for the problem (e.g., you will use matrix decomposition to solve this problem).
This makes it possible for the LLM to dynamically adapt its reasoning process as opposed to using predefined heuristics.
METASCALE
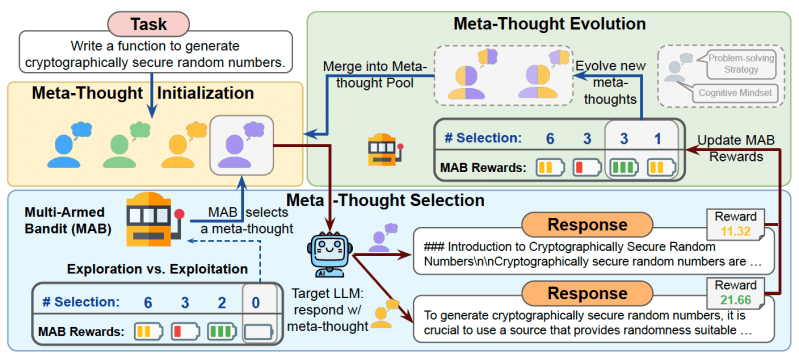
METASCALE builds on meta-thoughts and provides a prompt engineering framework that can be applied to any model to explore different reasoning strategies.
METASCALE operates in three steps:
1) The LLM is given the input prompt and instructed to generate a diverse pool of reasoning strategies. To help the LLM, METASCALE provides examples from instruction-tuning datasets that contain reasoning templates for different types of problems.
2) After generating the reasoning examples, METASCALE uses a Multi-Armed Bandit (MAB) algorithm to select the most promising reasoning strategy. MAB helps the system choose between exploring new options or sticking to the best-performing strategy.
3) Finally, a genetic algorithm iteratively refines and expands the pool of cognitive strategies by combining working strategies to create new ones.
METASCALE uses an iterative process to develop and refine the reasoning strategy for each prompt.
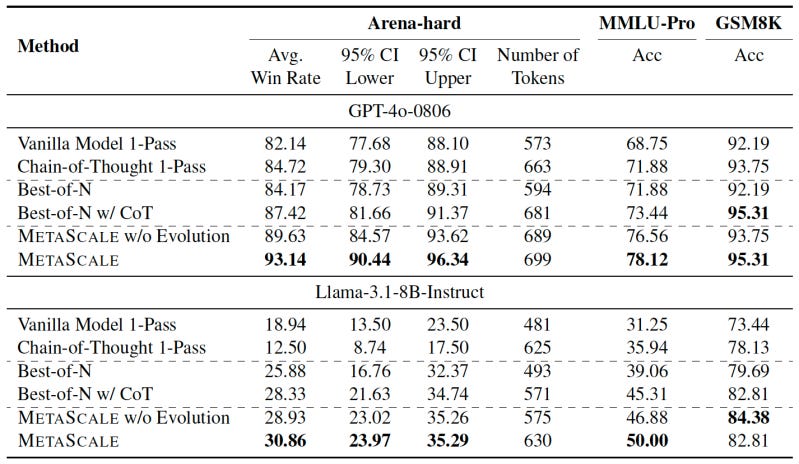
The researchers tested METASCALE on multiple benchmarks, including GSM8K, MMLU-Pro, and Arena-Hard, using GPT-4o and Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct as the backbone LLM. They compared it to four baseline inference methods: direct responses with 1-pass inference, classic chain-of-thought, Best-of-N, and Best-of-N with CoT.
METASCALE consistently outperforms baseline methods in all tasks. Notably, GPT-4o with METASCALE outperformed o1-mini under style control. METASCALE is also scalable and continues to improve as you sample more solutions.
"These results demonstrate that integrating meta-thoughts enables LLMs to scale more effectively during test time as the number of samples increases," the researchers write.